JFT 4/25/99
| Vocabulary | |
anion exothermic  ionic compound  valence electrons  valence shell 
|
In the case of sodium, ionizing the atom completely removes the 3s valence shell. The remaining electrons are tightly bound and require far more energy to remove. As a result, the sodium ion is far more inert than the sodium atom.
Table Some differences in chemical and physical properties for sodium ion and sodium atom.
| Property | Na atom | Na+ ion |
| charge | neutral (0) | positive (+1) |
| electronic configuration | 1s22s22p63s1 | 1s22s22p6 |
| pure form | soft, shiny metal | not found pure; must be combined with anions to form stable ionic compounds |
| reaction with water | violent exothermic reaction with water forms Na+(aq), OH-(aq), H2(g) | Na+ dissolves in water without further reaction |
| reaction with hydrogen gas | 2 Na(s) + H2(g) 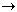 2 NaH(s) 2 NaH(s) |
no reaction |
| reaction with oxygen gas | 2 Na(s) + O2(g) 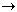 Na2O2(s) Na2O2(s) |
no reaction |
| reaction with alcohol | 2 Na(s) + 2 C2H5OH(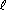 ) )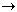 2 NaOC2H5 + H2(g) 2 NaOC2H5 + H2(g) |
no reaction |
| conductivity | Na(s) is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity | Na+ solid compounds are poor conductors of heat and electricity; Na+ in aqueous solution conducts electricity |
Author: Fred Senese senese@frostburg.edu