- What is thiosulfate ion?
- What are some common thiosulfate compounds?
- What are thiosulfates used for?
- How does thiosulfate ion affect health and the environment?
- What is the structure of the thiosulfate ion?
- Where does thiosulfate ion come from?
What is thiosulfate ion?
Thiosulfate (S2O32-) is an oxyanion of sulfur produced by the reaction of sulfite ions with elemental sulfur in boiling water, S2O3-2(aq)
S2O3-2(aq)
 that locks proteins into their correct three-dimensional shapes.
Thiosulfate is not found in large quantities in nature. Solutions of thiosulfate break down into sulfur, sulfites, and sulfates when exposed to acids, light, metal ions, and bacteria.
that locks proteins into their correct three-dimensional shapes.
Thiosulfate is not found in large quantities in nature. Solutions of thiosulfate break down into sulfur, sulfites, and sulfates when exposed to acids, light, metal ions, and bacteria.
Thiosulfate is a reducing agent. It is routinely used as a titrant to determine concentrations of oxidants such as hypochlorite in bleach and dissolved oxygen in water. It instantly dechlorinates water, and is used to stop bleaching action in the paper-making industry. Thiosulfate forms water-soluble complexes with many metals, making it useful in photoprocessing (where it dissolves excess silver bromide on the surface of exposed film, preventing excessive darkening). Thiosulfate is also useful in the extraction of silver from silver ore, in leather manufacture, and as a mordant in the textile industry.
What is the structure of the thiosulfate ion?
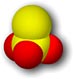
|
| Structure of the thiosulfate ion. Yellow = sulfur, Red = oxygen. Click the image for a 3D Chime model. |
 bonds,
so the S-S bond is somewhat longer than the S-O bonds (1.99 +/- 0.03 A vs. 1.48 +/- 0.06 A, respectively) [Nardelli].
bonds,
so the S-S bond is somewhat longer than the S-O bonds (1.99 +/- 0.03 A vs. 1.48 +/- 0.06 A, respectively) [Nardelli].
What are some common thiosulfate compounds?
| Formula | Name | Water Solubility | Uses | Resources |
| (NH4)2S2O3 | ammonium thiosulfate (ammo hypo, Amthio |
high | fungicide; fixative in photographic development; lubricants for metalworking; metal cleaning agent | |
| BaS2O3 | barium thiosulfate | slight | manufacture of explosives and matches; photographic processes | |
| CaS2O3 | calcium thiosulfate (Tecesal) |
high | liquid lime/sulfur agricultural treatments | |
| AuNa3(S2O3)2•2 H2O | gold(I) sodium thiosulfate dihydrate (Auricidine, Aurocidin; Aurolin; Auropex;Auropin; Aurosan; Aurothion) |
high | screening for gold allergies; antirheumatic | |
| K2S2O3 | potassium thiosulfate | high | fixative in photographic development; liquid lime/sulfur agricultural treatments | |
| Na2S2O3 | sodium thiosulfate (Hypo) |
high | fixative in photographic development; water dechlorination; paper manufacture; whitening agent | |
Solubility data compiled from the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC). Commercial and medical uses compiled from the Merck Index (Merck) and Web/paper references cited below. | ||||
What is thiosulfate used for?
Most of thiosulfate's usefulness stems from its ability to convert certain insoluble metal compounds into soluble complexes, and its ability to act as a mild reducing agent.- Photographic fixing agent.
An emulsion of sodium thiosulfate (called hypo by photographers) is used to stop development of exposed film. Thiosulfate converts undeveloped silver bromide grains in the film into water-soluble silver thiosulfate complexes that can be removed when the film is washed.
S2O32- + AgBr(s)
 AgS2O3- + Br-
AgS2O3- + Br-
S2O32- + AgS2O3-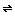 Ag(S2O3)3-
Ag(S2O3)3-
- Extracting silver from ores. Thiosulfate's ability to convert silver compounds into soluble silver complexes also makes it useful in ore processing.
- Paper manufacture and dechlorination of water.
Thiosulfate ion is used to remove chlorine (hypochlorite)
from water or from solutions used to bleach paper pulp:
HOCl + 2 S2O32-
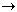 Cl- + S4O62- + OH-
Cl- + S4O62- + OH-
- Dissolved oxygen testing and chemical analysis of oxidants. Thiosulfate is a reducing titrant used for determining many oxidizing agents. For example, hypochlorite concentrations in bleach can be determined using the reaction above. Thiosulfate is also used as a titrant in determining biochemical oxygen demand (the extent to which oxygen within a sample can support microbial life) [RPI].
- Whitening cotton fabrics, bone, straw, and ivory. Some materials are weakened or yellowed when bleached. Thiosulfate solutions can sometimes be used to whiten these materials. See Garments: Discoloration/Yellowing from Age [NCSU]
How does thiosulfate ion affect health and the environment?
Thiosulfate is an antidote for cyanide poisoning. It reacts with cyanide to produce sulfite and thiocyanate ions:
CN- + S2O32- 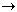 SCN- + SO32-
SCN- + SO32-
Thiosulfate is an intermediate in several biochemical pathways, including the synthesis of L-cysteine (an amino acid ).
Thiosulfate is manufactured by some cells by oxidation of elemental sulfur and by degradation of L-cysteine.
).
Thiosulfate is manufactured by some cells by oxidation of elemental sulfur and by degradation of L-cysteine.
Thiosulfates break down rapidly in the environment due to the action of air and certain bacteria, eventually producing sulfides and sulfates.
Where does thiosulfate ion come from?
Thiosulfate is produced industrially by several different reactions:- Reaction of sulfur with sodium sulfite in boiling aqueous solution,
S8 + 8 SO32-
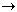 8 S2O32-
8 S2O32-
- Reaction of SO2 gas with sulfide/carbonate liquor (a byproduct of paper manufacturing).
- As a byproduct in the manufacture of sulfur dyes.
References and Resources
- Crystallographic structure of the thiosulfate ion (M. Nardelli, G. Fava)
- Acta Cryst., 15, 477 (1962).
- The Merck Index (Merck & Co., Inc.)
- An encyclopedia of drugs and chemicals. (8th ed., Rahway, NJ 1968.
- Thiosulfate (S. W. Dahwak)
- J. Chem. Ed., 70, 12 (1993).
- Garments: Discoloration/Yellowing from Age (NCSU)
- Chemical mixtures for fabric whitening.
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (RPI)
- Procedure for determining the extent to which oxygen in a sample can support microbial life. Thiosulfate is used as a titrant in the procedure.