Anhydrous sodium carbonate melts at 851°C (1124 K); however, it gradually decomposes in the temperature range you've specified,
according to
Na2CO3(s) 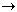 CO2(g) + Na2O(s)
CO2(g) + Na2O(s)
Sodium bicarbonate is even less stable with respect to heating. Solid NaHCO3 begins to lose carbon dioxide and water around 100°C, with complete conversion to sodium carbonate by 200°C:
2 NaHCO3(s) 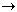 CO2(g) + H2O(g) + Na2CO3(s)
CO2(g) + H2O(g) + Na2CO3(s)
In aqueous solution, carbon dioxide production begins at room temperature and decomposition of NaHCO3(aq) is essentially complete if the solution is brought to boiling.
The ease with which sodium bicarbonate loses carbon dioxide on heating is what makes it useful as "baking soda" and as a component in baking powders; channels opened by escaping carbon dioxide bubbles give baked goods a lighter and fluffier texture.
References
- Y. Otsubo, K. Yamaguchi, J. Chem. Soc. Japan, 82, 557-560 (1961).
Author: Fred Senese senese@antoine.frostburg.edu

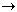 CO2(g) + Na2O(s)
CO2(g) + Na2O(s)
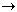 CO2(g) + H2O(g) + Na2CO3(s)
CO2(g) + H2O(g) + Na2CO3(s)