Ciske 1/19/99
Mercury (I) (or mercurous) compounds decompose on exposure to water into liquid mercury and mercury(II) (or mercuric) compounds. The equilibrium constant for the disproportionation of mercury(I) ion
Hg22+(aq) = Hg(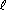 ) + Hg2+(aq)
) + Hg2+(aq)
Hg22+(aq) + S2-(aq) 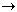 Hg(
Hg(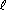 ) + HgS(s)
) + HgS(s)
| Name | Formula | Appearance | Decomposes on exposure to: |
| mercury(I) acetate | Hg2(C2H3O2)2 | flat sheetlike crystals | light, water |
| mercury(I) azide | Hg2(N3)2 | white crystals | shock, light, heat (explosive!) |
| mercury(I) bromate | Hg2(BrO3)2 | crystals | water, heat |
| mercury(I) bromide | Hg2Br2 | white tetrahedral crystals | light |
| mercury(I) carbonate | Hg2CO3 | yellow-brown crystals | light, heat, water |
| mercury(I) chloride (calomel) |
Hg2Cl2 | white tetrahedral crystals | light |
| mercury(I) chlorate | Hg2(ClO3)2 | white crystals | light |
| mercury(I) chromate | Hg2CrO4 | red needles or powder | heat |
| mercury(I) fluoride | Hg2F2 | yellow cubic crystals | light, heat (as liquid), water |
| mercury(I) formate | Hg2(CHO2)2 | shiny scales | heat, hot water |
| mercury(I) iodate | Hg2(IO3)2 | yellow powder | heat (at 250°C) |
| mercury(I) iodide | Hg2I2 | yellow tetrahedral crystals | light, heat (at 290°C) |
| mercury(I) nitrate | Hg2(NO3)2·2H2O | monoclinic crystals | light, water |
| mercury(I) nitrite | Hg2(NO2)2 | yellow | heat (at 100°C), water |
| mercury(I) oxide | Hg2O | black or brown-black powder | light, heat (at 100°C) |
| mercury(I) sulfate | Hg2SO4 | white-yellow powder | light, heat, water |
| mercury(I) sulfide | Hg2S | black solid | heat, water |
References
- F. A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Wiley Interscience, New York, 1988.
- The Merck Index, 8th ed., Merck & Co., 1968.
- The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 78th ed., eds. D. L. Lide and H.P.R. Frederikse, CRC Press, 1998
- The Merck Index, 8th ed., Merck & Co., 1968.
Resources
-
Mercury
| The qualitative analysis and characteristic reactions of mercury(I) and mercury(II) cations are described. Includes photographs of precipitates. http://www.public.asu.edu/~jpbirk/Qual/QUALANAL/Mercury.htm (01/19/99) |