
Home
Common Compounds
Exam Guide
FAQ
Features
Glossary
Construction Kits
Companion Notes
Just Ask Antoine!
Simulations
Slide Index
Toolbox
Tutorial Index
 Glossary
GlossaryGlossary: The quantum theory
- amplitude.

- The displacement of a wave from zero. The maximum amplitude for a wave is the height of a peak or the depth of a trough, relative to the zero displacement line.
- constructive interference. Compare with destructive interference
 .
. - When the peaks and troughs of two interfering
 waves match, the amplitudes add to give the resultant wave a higher amplitude.
waves match, the amplitudes add to give the resultant wave a higher amplitude. - destructive interference.
 Compare with constructive interference
Compare with constructive interference .
. - When the peaks of one wave match the troughs of another, the waves interfere
 destructively. The amplitudes
destructively. The amplitudes of the interfering waves cancel to give the resultant wave a lower amplitude.
of the interfering waves cancel to give the resultant wave a lower amplitude. - diffraction.
 diffract. Compare with effusion
diffract. Compare with effusion .
. - The ability of a wave to bend around the edges of obstacles or holes. The effect is most noticeable when the obstacle or hole is comparable to the size of the wavelength
 .
. - electromagnetic radiation.
 electromagnetic wave.
electromagnetic wave. - A wave
 that involves perpendicular oscillations in the electric and magnetic fields, moving at a speed of 2.99792458×108 m/s in a vacuum away from the source. gamma rays
that involves perpendicular oscillations in the electric and magnetic fields, moving at a speed of 2.99792458×108 m/s in a vacuum away from the source. gamma rays , x-rays
, x-rays , ultraviolet light
, ultraviolet light , visible light
, visible light , infrared radiation
, infrared radiation , and radio waves
, and radio waves are all electromagnetic waves.
are all electromagnetic waves. - frequency. (
 ) Compare with wavelength
) Compare with wavelength .
. - The number of cycles of a wave that move past a fixed observation point per second. The SI unit of frequency is the Hertz
 (Hz).
(Hz). - gamma rays. (
 -rays) gamma radiation.
-rays) gamma radiation. - A very high energy form of electromagnetic radiation
 , typically with wavelengths
, typically with wavelengths of less than 3 pm. Gamma rays are produced by certain nuclear decay processes, and are used to sterilize food.
of less than 3 pm. Gamma rays are produced by certain nuclear decay processes, and are used to sterilize food. - Hertz. (Hz, s-1) frequency.
- The SI unit of frequency
 , equal to one cycle of the wave per second (s-1).
, equal to one cycle of the wave per second (s-1). - infrared radiation. (IR) infrared.
- Electromagnetic radiation
 with wavelength
with wavelength longer than visible light but shorter than that of microwaves
longer than visible light but shorter than that of microwaves . Infrared radiation is produced by hot objects; absorption of infrared radiation causes chemical bonds to vibrate.
. Infrared radiation is produced by hot objects; absorption of infrared radiation causes chemical bonds to vibrate. - interference. interfering. Compare with constructive interference
 and destructive interference
and destructive interference .
. - The amplitudes
 of waves
of waves moving into the same region of space add to produce a single resultant wave. The resultang wave can have higher or lower amplitude than the component waves. See constructive interference
moving into the same region of space add to produce a single resultant wave. The resultang wave can have higher or lower amplitude than the component waves. See constructive interference and destructive interference
and destructive interference .
. - microwave. microwave radiation.
- Electromagnetic radiation
 with wavelength
with wavelength between 3 mm and 30 cm.
between 3 mm and 30 cm. - momentum. (p)
- Momentum is a property that measures the tendency of a moving object to keep moving in the same direction. Increasing the speed of an object increases its momentum, and a heavy object will have more momentum than a lighter one moving at the same speed. For a particle with mass m and velocity v, the momentum of the particle is mv.
- node.
- A point, region, or surface where the amplitude
 of a standing wave is zero. The probability of finding an electron at an orbital
of a standing wave is zero. The probability of finding an electron at an orbital node is zero.
node is zero. - phase. in phase; out of phase; wave phase.
- 1.A phase is a part of a sample of matter that is in contact with other parts but is separate from them. Properties within a phase are homogeneous (uniform). For example, oil and vinegar salad dressing contains two phases: an oil-rich liquid, and a vinegar-rich liquid. Shaking the bottle breaks the phases up into tiny droplets, but there are still two distinct phases. 2. In wave motion, phase is the fraction of a complete cycle that has passed a fixed point since the current cycle began. The phase is often expressed as an angle, since a full cycle is 360^deg; (2
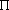 ). Two waves are "in phase" if the peaks of one wave align with the peaks of the other; they are "out of phase" if the peaks of one wave align with the troughs of the other.
). Two waves are "in phase" if the peaks of one wave align with the peaks of the other; they are "out of phase" if the peaks of one wave align with the troughs of the other. - photoelectric effect.
- Ejection of electrons from an atom or molecule that has absorbed a photon
 of sufficient energy. The photoelectric effect is the operating principle behind "electric eyes"; it is experimental evidence for particle-like behavior of electromagnetic radiation
of sufficient energy. The photoelectric effect is the operating principle behind "electric eyes"; it is experimental evidence for particle-like behavior of electromagnetic radiation .
. - photoelectron.
- An electron
 ejected from an atom or molecule that has absorbed a photon
ejected from an atom or molecule that has absorbed a photon .
. - photon. (h
 ) quantum; quanta.
) quantum; quanta. - A discrete packet of energy associated with electromagnetic radiation. Each photon carries energy E proportional to the frequency

 of the radiation: E = h
of the radiation: E = h , where h is Planck's constant
, where h is Planck's constant .
. - Planck's constant. (h)
- A proportionality constant that relates the energy carried by a photon
 to its frequency
to its frequency . Planck's constant has a value of 6.6262 × 10-34 J s.
. Planck's constant has a value of 6.6262 × 10-34 J s. - quantum. quanta.
- A discrete packet of energy.
- quantum mechanics. quantum theory.
- A branch of physics that describes the behavior of objects of atomic and subatomic size.
- quantum number.
- Indices that label quantized energy states. Quantum numbers are used to describe the state of a confined electron, e. g. an electron in an atom.
- ultraviolet light. ultraviolet; ultraviolet radiation; ultraviolet region; UV.
- Electromagnetic radiation
 with wavelength longer than that of x-rays
with wavelength longer than that of x-rays but shorter than that of visible light
but shorter than that of visible light . Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage.
. Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage. - uncertainty principle. Heisenberg's uncertainty principle; Heisenberg principle; indeterminancy; indeterminancy principle.
- The exact momentum and exact location of a particle cannot be specified. Werner Heisenberg stated that the product of uncertainties in location and momentum measurements can never be smaller than h/4
 , where h is Planck's constant
, where h is Planck's constant .
. - visible light.
- Visible light is electromagnetic radiation
 with a wavelength
with a wavelength between 400 and 750 nm.
between 400 and 750 nm. - wavefunction. (
 )
) - A mathematical function that gives the amplitude
 of a wave as a function of position (and sometimes, as a function of time and/or electron spin). Wavefunctions are used in chemistry to represent the behavior of electrons bound in atoms or molecules.
of a wave as a function of position (and sometimes, as a function of time and/or electron spin). Wavefunctions are used in chemistry to represent the behavior of electrons bound in atoms or molecules. - wavelength.
- The distance between adjacent peaks (or adjacent troughs) on a wave
 . Varying the wavelength of light changes its color; varying the wavelength of sound changes its pitch.
. Varying the wavelength of light changes its color; varying the wavelength of sound changes its pitch. - wave.
- An oscillating motion that moves outward from the source of some disturbance (ripples running away from a pebble tossed in a pond). Waves transmit the energy of the disturbance away from its source.
- x-ray.
- A very high energy form of electromagnetic radiation
 (though not as high energy as gamma rays
(though not as high energy as gamma rays ). X-rays typically have wavelengths from a few picometers up to 20 nanometers. X-rays easily penetrate soft tissue, which makes them useful in medical imaging and in radiation therapy.
). X-rays typically have wavelengths from a few picometers up to 20 nanometers. X-rays easily penetrate soft tissue, which makes them useful in medical imaging and in radiation therapy. - x-ray diffraction pattern.
- Interference patterns created by x-rays as they pass through a solid material. Studying x-ray diffraction
 patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms.
patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms. - x-ray spectrum. x-ray spectra.
- A set of characteristic x-ray
 frequencies
frequencies or wavelengths
or wavelengths produced by a substance used as a target in an x-ray tube
produced by a substance used as a target in an x-ray tube . Each element has a characteristic x-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number
. Each element has a characteristic x-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number and the frequencies of certain lines in the x-ray spectrum.
and the frequencies of certain lines in the x-ray spectrum. - x-ray tube.
- A cathode ray tube that focuses energetic streams of electrons on a metal target, causing the metal to emit x-rays
 .
. - zero point energy.
- A minimum possible energy for an atom or molecule predicted by quantum mechanics
 . Electrons stay in motion and bonds continue to vibrate even at absolute zero
. Electrons stay in motion and bonds continue to vibrate even at absolute zero because of zero point energy.
because of zero point energy.
General Chemistry Online! The quantum theory
Copyright © 1997-2010 by Fred Senese
Comments & questions to fsenese@frostburg.edu
Last Revised 02/23/18.URL: http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/quantum/glossary.shtml