Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) 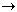 H2(g) + MgCl2(aq)
H2(g) + MgCl2(aq)
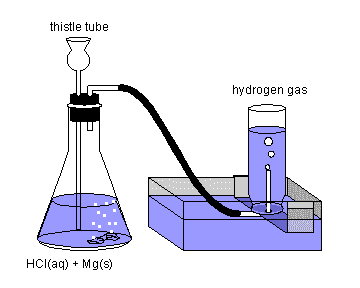
The trough is filled with water, and a wide mouth bottle is completely filled with water and inverted on the shelf. Magnesium or zinc metal is placed in the bottom of the flask and the acid (3 M HCl) is introduced through the thistle tube (which is just a long-stemmed funnel). Fill the flask with enough solution to cover the bottom of the thistle tube as shown to prevent air from entering and hydrogen from escaping through the funnel. Hydrogen gas will begin to escape from the rubber tube; allow the reaction to run for a few minutes before connecting it to the inverted bottle as shown, to sweep air out of the flask.
The collected hydrogen will be saturated with water vapor and contaminated with small amounts of air. You can force the gas through a tube packed with calcium chloride pellets to remove the water. Hydrogen can be further purified by exploiting the fact that the gas is extremely soluble in many solid metals. The metal palladium (Pd) is especially good at dissolving hydrogen. If the gas is forced through a tube blocked by a membrane of palladium, hydrogen passes through the membrane but the gaseous impurities do not.
To determine the purity of a sample of dried hydrogen, you can burn it in excess dry oxygen and pass it through a tube packed with a strong dehydrating agent like Dehydrite or Anhydrone. The weight increase of the tube gives the amount of water produced by the combustion reaction, and so, the amount of hydrogen in the sample. There are many technical difficulties that need to be considered to get good results by this method; see Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, AOAC, 13th ed., 1980, pp 855-857 for more details. Hydrogen has a distinctive line spectrum, and it can be qualitatively and quantitatively detected using emission spectroscopy.
The laboratory preparation using magnesium or zinc is too expensive for industrial production of hydrogen. Hydrogen is produced more cheaply by the reaction of iron with steam at about 600°C.
3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g) 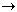 Fe3O4(s) + 4 H_2(g)
Fe3O4(s) + 4 H_2(g)
Hydrogen can also be produced by passing a strong electric current through water:
2 H2O(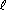 )
) 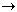 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
2 H2(g) + O2(g)