
Home
Common Compounds
Exam Guide
FAQ
Features
Glossary
Construction Kits
Companion Notes
Just Ask Antoine!
Simulations
Slide Index
Toolbox
Tutorial Index
Introduction
Measurement
Matter
Atoms & ions
Compounds
Chemical change
The mole
Gases
Energy & change
The quantum theory
Electrons in atoms
The periodic table
Chemical bonds
Solids
Liquids
Solutions
| Acids & bases |
Reaction rates
Organic chemistry
Everyday chemistry
Inorganic chemistry
Environmental chemistry
Laboratory
History of chemistry
Miscellaneous
Home  FAQ FAQ  Acids and bases Acids and bases | Print | Comment |
| Previous Question | Next Question |
How is pKa related to pKb?
- How can I find a relationship to pKa and pKb using pK = - log K ?
Alex Baskin baskin@scruznet.com -
Imagine you have an acid dissociation
followed by hydrolysis of the A- ion,HA 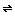 H+ + A-
H+ + A-

Ka = [H+][A-]
[HA]
If you add the two reactions together, the net reaction is the hydrolysis of water,A- + H2O 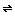 HA + OH-
HA + OH-

Kb = [OH-][HA]
[A-]
Looking at the equilibrium expressions, you can see that the product of Ka and Kb is Kw:H2O 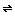 H+ + OH-
H+ + OH-
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.01×10-14
Take minus the log of both sides of this equation and you get pKa + pKb = pKw.Ka Kb = [H+][A-]
[HA]× [OH-][HA]
[A-]= [H+][OH-] = Kw
Back to Just Ask Antoine!