
Home
Common Compounds
Exam Guide
FAQ
Features
Glossary
Construction Kits
Companion Notes
Just Ask Antoine!
Simulations
Slide Index
Toolbox
Tutorial Index
Introduction
Measurement
Matter
Atoms & ions
Compounds
| Chemical change |
Gases
Energy & change
The quantum theory
Electrons in atoms
The periodic table
Chemical bonds
Solids
Liquids
Solutions
Acids & bases
Redox reactions
Reaction rates
Organic chemistry
Everyday chemistry
Inorganic chemistry
Environmental chemistry
Laboratory
History of chemistry
Miscellaneous
Home  FAQ FAQ  Chemical change Chemical change | Print | Comment |
| Previous Question | Next Question |
How should the reaction between vinegar and baking soda be classified?
- What kind of a chemical reaction occurs when acetic acid (vinegar) and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) are mixed- combination, decomposition, displacement, or double displacement?
Melissa Mattes 1/13/99 -
A double displacement reaction (also called a double decomposition or metathesis reaction) has the form
AB + CD
where A, B, C, and D are atoms or ions. The reaction between vinegar and baking soda can be written as a double displacement reaction if carbonic acid (H2CO3) is considered a product: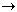 AC + BD
AC + BD
HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHCO3(aq)
Here A, B, C, and D are H+, C2H3O2-, Na+, and HCO3-, respectively. [1, 2]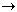 NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2CO3(aq)
NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2CO3(aq)
However, carbonic acid readily decomposes into carbon dioxide and water,
H2CO3(aq)
and the carbon dioxide can escape from the solution as a gas.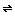 CO2(aq) + H2O(
CO2(aq) + H2O( )
)
The combined equation is
HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHCO3(aq)
which doesn't fit neatly into one category, since it is a double displacement followed by a decomposition. When you encounter a reaction that is difficult to classify, consider the possibility that it may be the net or total equation for a sequence of steps.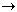 NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(
NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2O( ) + CO2(g)
) + CO2(g)
Notes
- For double displacement reactions in aqueous solution, there is an additional requirement: if all of the products are soluble, strong electrolytes, then no reaction occurs. H2CO3 is a weak acid and so, a weak electrolyte. You can see the reason for this additional requirement when you try to write the net ionic equation for a reaction that involves only strong electrolytes: all of the ions are spectator ions in that case, and there is no net ionic equation.
- The reaction can also be classified as a neutralization since a hydrogen ion is donated by one reactant and accepted by another. Back
General Chemistry Online! How should the reaction between vinegar and baking soda be classified?
Copyright © 1997-2010 by Fred Senese
Comments & questions to fsenese@frostburg.edu
Last Revised 02/23/18.URL: http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/reactions/faq/classify-vinegar-bakingsoda.shtml