
Home
Common Compounds
Exam Guide
FAQ
Features
Glossary
Construction Kits
Companion Notes
Just Ask Antoine!
Simulations
Slide Index
Toolbox
Tutorial Index
 Glossary
GlossaryGlossary: U
- ultraviolet light. ultraviolet; ultraviolet radiation; ultraviolet region; UV.
- Electromagnetic radiation
 with wavelength longer than that of x-rays
with wavelength longer than that of x-rays but shorter than that of visible light
but shorter than that of visible light . Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage.
. Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage. - uncertainty principle. Heisenberg's uncertainty principle; Heisenberg principle; indeterminancy; indeterminancy principle.
- The exact momentum and exact location of a particle cannot be specified. Werner Heisenberg stated that the product of uncertainties in location and momentum measurements can never be smaller than h/4
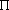 , where h is Planck's constant
, where h is Planck's constant .
. - unimolecular reaction.
- A reaction that involves isomerization
 or decomposition
or decomposition of a single molecule.
of a single molecule. - unit.
- A standard for comparison in measurements. For example, the meter
 is a standard length which may be compared to any object to describe its length.
is a standard length which may be compared to any object to describe its length. - unit cell.
- The simplest arrangement of atoms or molecules that regularly repeats in a crystal structure.
- universal indicator.
- A universal indicator is an indicator
 which undergoes several color changes over a wide range of pH
which undergoes several color changes over a wide range of pH . The color is used to "indicate" pH directly. Universal indicators are usually mixtures of several indicators.
. The color is used to "indicate" pH directly. Universal indicators are usually mixtures of several indicators.
- unpaired spin. (
 ) unpaired electron. Compare with paired spin
) unpaired electron. Compare with paired spin .
. - A single electron occupying an orbital
 .
. - unsaturated compound.
- An organic compound with molecules containing one or more double bonds.
- unsaturated fat. Compare with saturated fat
 .
. - A lipid
 containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Unsaturated fats tend to be oily liquids and are obtained from plants.
containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Unsaturated fats tend to be oily liquids and are obtained from plants. - unsaturated solution. Compare with saturated solution
 .
. - A solution with a concentration lower than its equilibrium solubility
 .
.

General Chemistry Online! Glossary: U
Copyright © 1997-2010 by Fred Senese
Comments & questions to fsenese@frostburg.edu
Last Revised 02/23/18.URL: http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/glossary/u.shtml